Why Does Your Pressure Transmitter Not Work?
From: Issued date 2024.12.06 Back
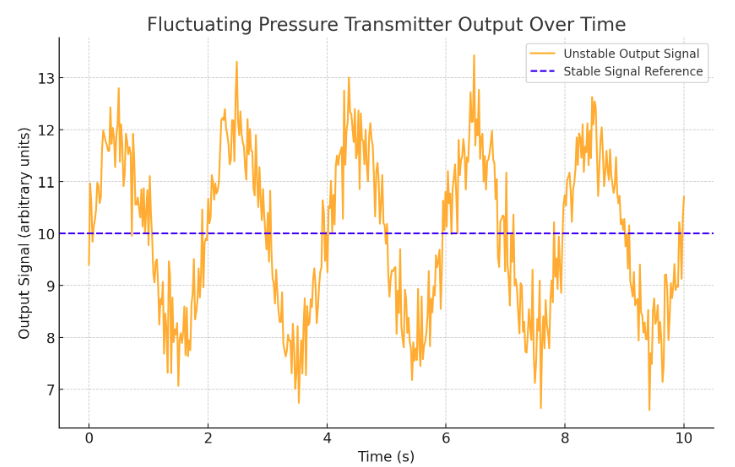
The graph illustrates an example of an unstable pressure transmitter output. The fluctuations and noise represent potential issues caused by weak anti-interference, loose wiring, or other factors mentioned. The dashed purple line indicates the expected stable output for reference.
Pressure transmitters often experience issues that can be diagnosed and resolved using systematic methods. Here's a summary of common problems and their solutions:
1. Pressure Does Not Change
Symptoms: Pressure increases but transmitter output remains static or changes suddenly; zero position doesn't reset after depressurization.
Troubleshooting Steps:
Check for leaks or blockages in the pressure interface.
Verify wiring and power supply.
Test the sensor's zero position output.
Gradually increase pressure to determine if the sensor is damaged.
Consider system or instrument damage.
2. Output Signal is Unstable
Possible Causes:
Unstable pressure source.
Weak anti-interference ability of sensor or instrument.
Loose wiring or vibration.
Sensor failure.
3. Output Does Not Change Initially
Cause: Sealing ring blocks the pressure inlet.
Solution:
Remove sensor and check the zero point.
Replace the sealing ring with a suitable composite gasket.
4. No Output
Possible Causes:
Incorrect wiring.
Open or short circuit.
Power mismatch.
Instrument or sensor damage.
5. Transmitter Error
Example Error Calculation:
Normal error = 30×1.5%+0.2×0.5=0.55bar.
For a 30 bar gauge with 1.5% accuracy and 0.2 bar minimum scale
6. Water Entry
Causes:
Loose meter cover.
Poor sealing of cable or shell plug.
Upside-down installation.
Three tips to make your sensor work properly
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Replacement | Swap faulty transmitter with a functional one to isolate the issue. |
| Disconnecting | Separate components to identify fault location. |
| Short Circuit Test | Test system by bypassing parts safely (e.g., test for blockages by bypassing pressure pipes). |