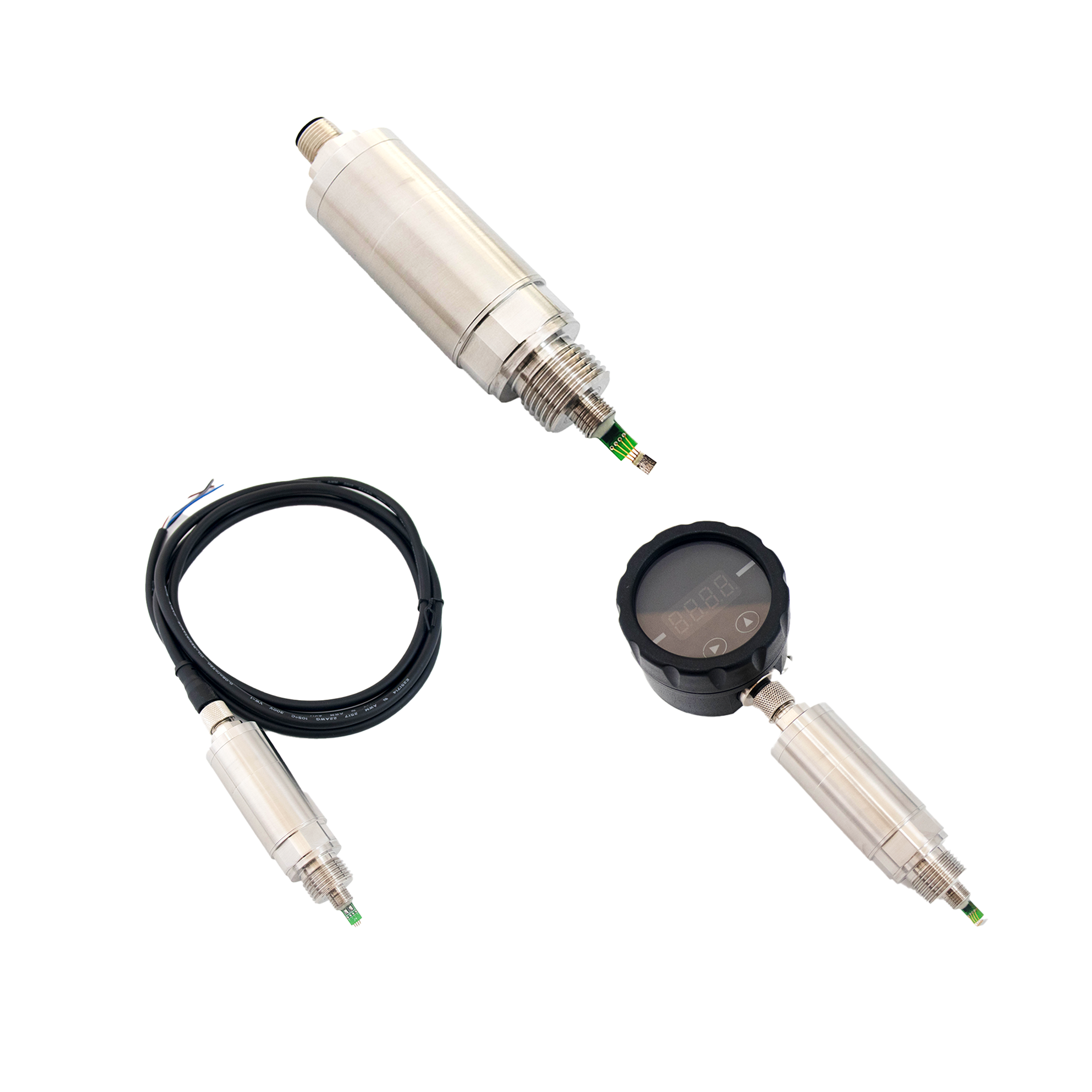
The Role of Pressure Transmitters in Steam, Gas, Petrochemical, and Firefighting Systems
From: Issued date 2025.02.26 Back
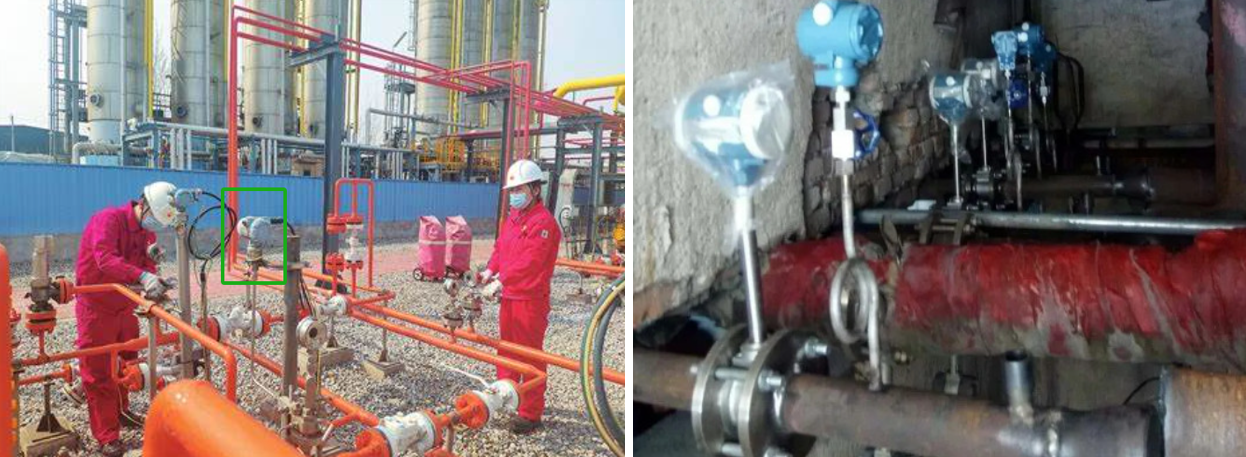
Pressure transmitters are critical components in industrial systems that require accurate monitoring and control of pressure. Whether in steam piping, natural gas pipelines, petrochemical plants, or firefighting piping systems, pressure transmitters ensure the smooth and efficient operation of industrial processes. These systems, which often operate under extreme pressure, temperature, and potentially hazardous conditions, rely on pressure transmitters to ensure safety, optimize performance, and prevent costly downtime.
Pressure Transmitters in Steam Piping Systems
Key Considerations for Steam Pressure Transmitters
High-Temperature Resistance: Steam systems require transmitters capable of operating in extreme temperature environments. Pressure transmitters must be constructed with high-temperature-resistant materials such as stainless steel or Inconel to withstand the elevated temperatures.
Vibration and Thermal Cycling: Steam systems often involve significant vibration due to pumps and compressors. The pressure transmitters need to be vibration-resistant and capable of withstanding thermal cycling, where the system undergoes frequent heating and cooling.
Corrosion Resistance: Steam often carries moisture and condensate, which can be corrosive. Therefore, pressure transmitters need to be made from materials that resist corrosion, such as 316 stainless steel.
Accuracy and Calibration: Precision in measuring steam pressure is essential, as inaccuracies can lead to system inefficiencies or dangerous pressure conditions. In these high-stakes systems, accurate pressure transmitters are often equipped with remote seals and self-diagnostic features to ensure continued reliability.
Role of Pressure Transmitters in Steam Systems
Pressure transmitters in steam piping systems monitor steam pressure to control the operation of boilers, turbines, and heat exchangers. By keeping the pressure within a safe range, these transmitters prevent dangerous overpressure situations, which could lead to equipment failure or safety hazards.
Pressure Transmitters in Natural Gas Pipelines
Key Considerations for Natural Gas Pressure Transmitters
High Pressure Handling: Pressure transmitters in natural gas pipelines must be able to withstand high-pressure environments while maintaining accuracy. Gas pressure must be monitored and regulated to prevent leaks or over-pressurization that could damage the pipeline or create a hazardous situation.
Explosion-Proof Design: Given that natural gas is highly flammable, the transmitters must often be designed to be explosion-proof or intrinsically safe to prevent ignition in the event of a leak.
Corrosion Resistance: Since natural gas pipelines can carry impurities or moisture, the pressure transmitters need to be resistant to corrosion and capable of operating in harsh environments.
Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics: In large pipeline networks, remote monitoring of pressure conditions is crucial. Pressure transmitters are often equipped with digital communication protocols such as HART, Modbus, or Profibus, allowing operators to monitor pressure levels remotely and make adjustments from a control room.
Role of Pressure Transmitters in Gas Pipelines
Pressure transmitters in gas pipelines ensure that gas is transported at the right pressure, preventing overpressurization, which could damage equipment or create dangerous conditions. Accurate pressure measurements are crucial to avoid leaks, and remote monitoring allows for better system control and predictive maintenance.
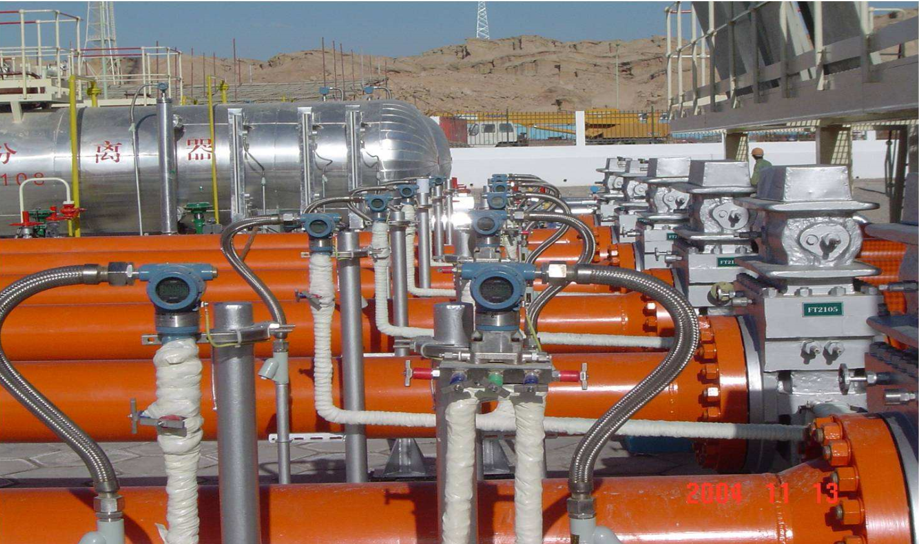
Pressure Transmitters in Petrochemical Plants
Key Considerations for Petrochemical Pressure Transmitters
Chemical Resistance: Petrochemical processes involve aggressive chemicals that can be corrosive to metal components. As such, pressure transmitters must be made of materials that resist corrosion and chemical attack, such as Hastelloy or Tantalum.
High Pressure and Temperature Resistance: Like steam systems, petrochemical plants operate under extreme conditions, often with high temperatures and pressures. Pressure transmitters must be capable of handling these extreme conditions while maintaining high accuracy.
Explosion-Proof or Intrinsically Safe: Many petrochemical processes are carried out in hazardous areas where the potential for explosion exists. Pressure transmitters must often be certified as explosion-proof to ensure safety.
Remote Diagnostics and Control: Due to the complexity of petrochemical systems, transmitters are equipped with remote diagnostics and integrated communication protocols that allow operators to monitor system pressure and detect potential issues before they become critical.
Role of Pressure Transmitters in Petrochemical Plants
In petrochemical plants, pressure transmitters are used to monitor pressure levels in reactors, distillation columns, and pipelines to prevent overpressure situations that could lead to equipment failure or accidents. Maintaining proper pressure levels is essential for the safe and efficient processing of chemicals and fuels.
Pressure Transmitters in Firefighting Piping Systems
Key Considerations for Firefighting Pressure Transmitters
Accuracy: Firefighting systems rely on accurate pressure monitoring to ensure that sufficient pressure is available when needed. Pressure transmitters help ensure that the system maintains the correct pressure for firefighting operations.
Durability and Reliability: Firefighting systems must be able to withstand harsh conditions, especially in outdoor environments. Pressure transmitters need to be designed for ruggedness, with weatherproof or explosion-proof casings to handle rough handling and environmental factors.
Low Maintenance: Since firefighting systems are standby systems (activated in emergencies), pressure transmitters must require minimal maintenance. They should be highly reliable and have the ability to self-diagnose to ensure they remain operational over long periods without intervention.
Role of Pressure Transmitters in Firefighting Systems
Pressure transmitters in firefighting piping systems ensure that water or foam is delivered at the proper pressure to suppress fires effectively. These systems often operate at high pressure (typically 150 psi to 250 psi) and require constant monitoring to ensure they are always ready for emergency use.
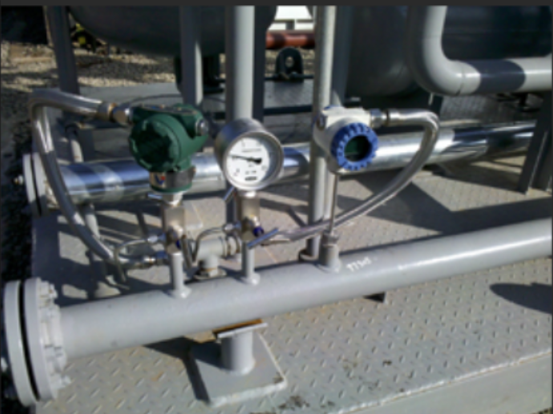
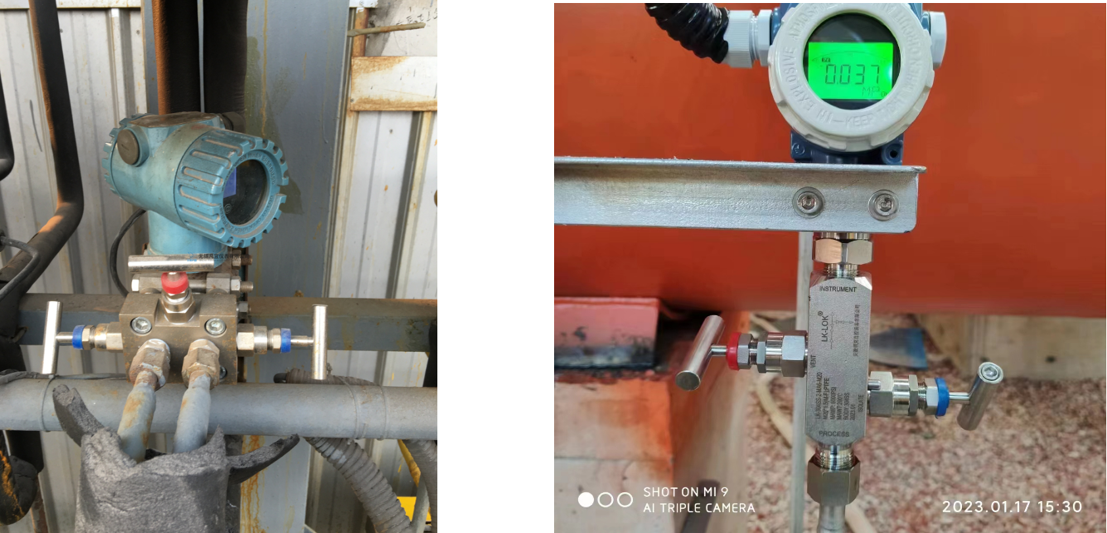
Three-Valve Manifolds and Second Valve Groups: Key Accessories for Pressure Transmitters
Three-Valve Manifold
A three-valve manifold is used to isolate, equalize, and vent the pressure transmitter during maintenance, calibration, and troubleshooting. The manifold consists of three valves:
Isolation Valves: These valves isolate the pressure transmitter from the process, allowing for safe maintenance without affecting the system.
Equalizing Valve: This valve equalizes the pressure between the transmitter and the process, preventing pressure spikes when the transmitter is isolated.
Venting Valve: The vent valve allows for safe venting of trapped fluids or gases.
Three-valve manifolds are ideal for high-pressure systems like steam and natural gas pipelines, where accurate pressure measurements and system isolation are critical.
Second Valve Group (Two-Valve Manifold)
A second valve group (two-valve manifold) provides isolation and venting but lacks the equalizing valve found in the three-valve manifold. This simpler configuration is typically used in less demanding applications where regular calibration and equalization are not necessary, such as in firefighting piping systems or low-pressure steam systems.
Pressure transmitters are essential for maintaining safety, efficiency, and operational reliability in steam piping, natural gas pipelines, petrochemical plants, and firefighting systems. They ensure that pressure levels remain within the correct range