The Role of Pressure Sensors in the Food Industry
From: Issued date 2025.03.07 Back
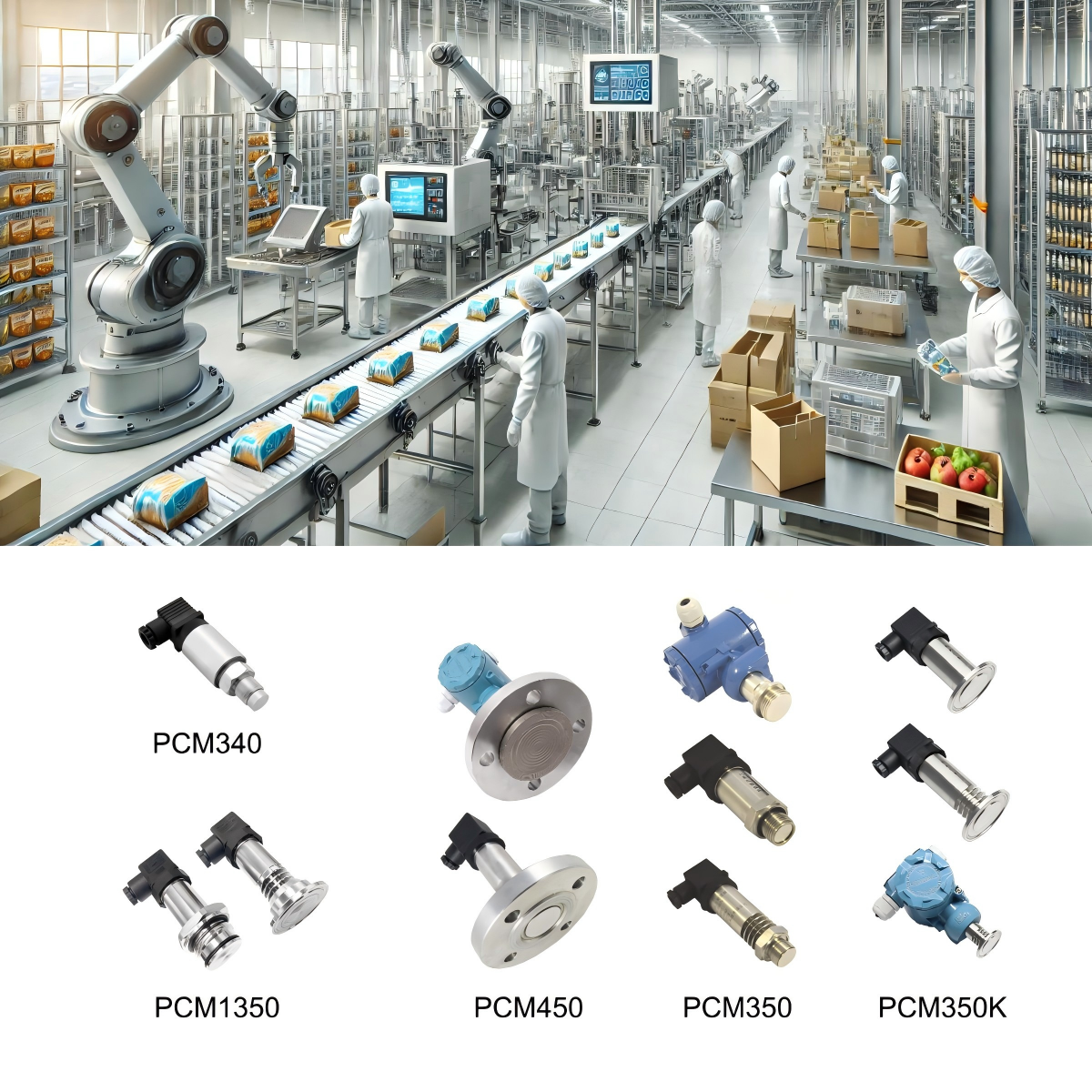

Pressure sensors play a pivotal role in the food and beverage industry, ensuring the efficiency, safety, and quality of various processes. As automation becomes increasingly prevalent, the reliance on accurate and reliable pressure measurements has grown substantially. This article delves into the applications of pressure sensors within the food industry, offers guidance on selecting the appropriate sensor for specific equipment, and explores future trends shaping the sector.
Applications of Pressure Sensors in the Food Industry
Pressure sensors are integral to numerous processes in the food and beverage sector, including:
1. Process Monitoring and Control: Maintaining optimal pressure is essential in processes like pasteurization, sterilization, and carbonation. Pressure sensors ensure that these processes operate within specified parameters, guaranteeing product safety and consistency.
2. Tank Level Measurement: By measuring the hydrostatic pressure exerted by liquid columns, pressure sensors can accurately determine the fill levels in storage and mixing tanks, aiding in inventory management and process control.
3. Pump and Filter Monitoring: Monitoring the pressure across pumps and filters helps in assessing their performance and detecting blockages or wear, thereby facilitating timely maintenance and reducing downtime.
4. Clean-in-Place (CIP) Systems: CIP systems rely on pressure sensors to monitor and control the flow and pressure of cleaning agents, ensuring thorough sanitation without disassembling equipment.
Selecting the Right Pressure Sensor for Food Equipment
Choosing an appropriate pressure sensor necessitates careful consideration of various factors:
1. Hygienic Design: Sensors must adhere to stringent sanitary standards to prevent contamination. Features like smooth surfaces, stainless steel construction, and compliance with certifications such as EHEDG and 3-A Sanitary Standards are crucial. citeturn0search12
2. Measurement Range and Accuracy: The sensor's pressure range should align with the application's requirements, ensuring accurate readings without compromising sensor integrity.
3. Temperature Compatibility: Given the high-temperature processes like sterilization, sensors should withstand elevated temperatures without performance degradation.
4. Chemical Resistance: Sensors must resist corrosion from various cleaning agents and food products to maintain longevity and reliability.
5. Process Connection: Compatible fittings, such as tri-clamp or DIN connections, ensure seamless integration into existing equipment.
6. Environmental Protection: A high IP (Ingress Protection) rating safeguards sensors against moisture and particulate ingress, which is vital in washdown environments.
7. Signal Output: Compatibility with control systems is essential. Common outputs include analog signals (4-20 mA) and digital interfaces (HART, Modbus).
Market Trends and Product Specialization
The pressure sensor market within the food industry has experienced notable growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing automation. Key trends include:
1. Integration of MEMS Technology: Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) have enabled the development of compact, cost-effective, and highly sensitive pressure sensors, facilitating their widespread adoption.
2. Smart Sensors and IoT Connectivity: The advent of Industry 4.0 has led to the incorporation of smart sensors capable of real-time data transmission and diagnostics, enhancing process monitoring and predictive maintenance.
3. Emphasis on Energy Efficiency: Manufacturers are focusing on sensors with low power consumption to align with sustainability goals and reduce operational costs.
4. Customization and Application-Specific Designs: There is a growing demand for sensors tailored to specific applications, such as high-viscosity fluids or abrasive materials, ensuring optimal performance under unique conditions.
Future Outlook of Pressure Sensors in the Food Industry
The future of pressure sensors in the food industry is poised for significant advancements:
1. Enhanced Connectivity: The proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT) will lead to more interconnected sensors, enabling comprehensive data analytics and more efficient process control.
2. Artificial Intelligence Integration: Combining pressure sensor data with AI algorithms can facilitate predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and process optimization, leading to improved efficiency and reduced waste.
3. Advancements in Materials: The development of new materials will result in sensors with greater durability, chemical resistance, and suitability for extreme conditions, expanding their application scope.
4. Sustainability Focus: Future sensors will likely be designed with an emphasis on environmental impact, including energy-efficient operation and eco-friendly materials, aligning with global sustainability initiatives.
5. Regulatory Compliance: As food safety standards become more stringent, sensors will need to evolve to meet higher regulatory requirements, ensuring consumer safety and maintaining brand reputation.
Pressure sensors are indispensable in the food and beverage industry, contributing to process efficiency, product quality, and safety. Selecting the appropriate sensor involves a thorough understanding of application requirements and environmental conditions. With ongoing technological advancements and a focus on connectivity and sustainability, pressure sensors will continue to evolve, offering enhanced capabilities and supporting the industry's dynamic landscape.