Guide to Pressure Transmitter Selection
From: Issued date 2024.11.28 Back

A pressure transmitter is a device that converts pressure into an electrical signal, making it a crucial tool in various industrial control systems due to its simple design, reliability, high accuracy, and wide measurement range; commonly used across industries like hydropower, railway transportation, smart buildings, manufacturing, aerospace, and oil & gas, where precise pressure monitoring is essential for efficient operations and safety measures; this article will explore key aspects of selecting, using, and troubleshooting different types of pressure transmitters in various industrial applications.
Key points about pressure transmitters:
Function:
Measures pressure of liquids or gases by converting it into an electrical signal that can be read by a control system.
Benefits of WT pressure transmitters:
· High accuracy: Provides precise pressure readings, crucial for process control.
· Wide measurement range: Capable of measuring pressures across a broad spectrum.
· Robustness: Can withstand harsh environments and vibrations.
· Stability: Consistent readings over time with minimal drift.
· Good linearity: Output signal directly proportional to pressure change.
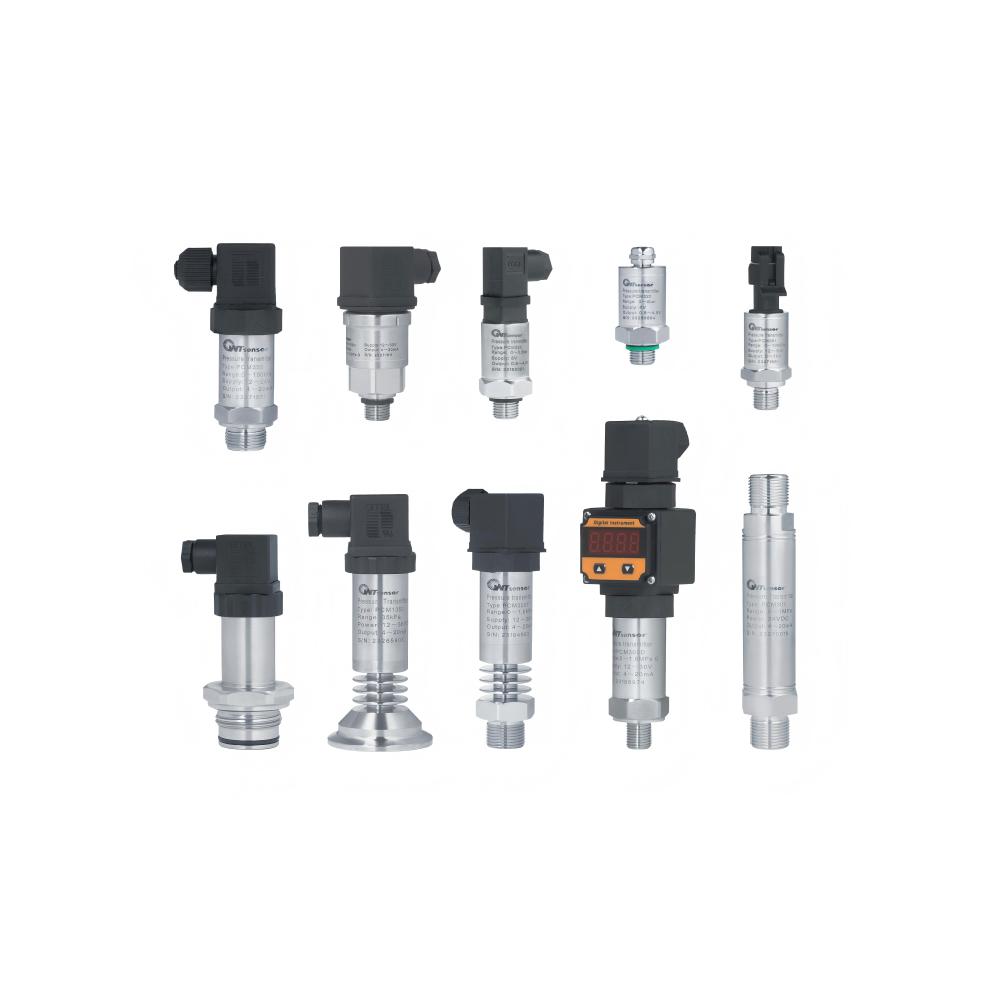
Common types of pressure transmitters:
· Gauge pressure: Measures pressure relative to atmospheric pressure.
· Absolute pressure: Measures pressure relative to a perfect vacuum.
· Differential pressure: Measures the pressure difference between two points.
· Industrial applications of pressure transmitters:
· Oil and Gas: Monitoring pressure in pipelines, wells, and processing plants
· Chemical Processing: Maintaining pressure levels in reactors and storage tanks
· Power Generation: Monitoring pressure in boilers and turbines
· Water Treatment: Regulating pressure in water distribution systems
· Aerospace: Measuring pressure in aircraft systems
· Machine Tools: Monitoring hydraulic pressure in machining processes
How to Select a pressure transmitter?
· Pressure range: Choose a transmitter with a measurement range suitable for the application.
· Accuracy requirements: Select a transmitter with the necessary precision level.
· Process conditions: Consider factors like temperature, pressure, corrosive fluids, and vibration.
· Output signal: Choose a compatible signal type for the control system.
· Sensor technology: Different sensor types (e.g., piezoelectric, strain gauge) have different advantages depending on the application.
This article Tags: pressure sensor pressure transmitter
Back to List