Exploring Electrostatic Immunity: Understanding and Testing for a Shock-Free Environment
From: Issued date 2023.11.30 Back
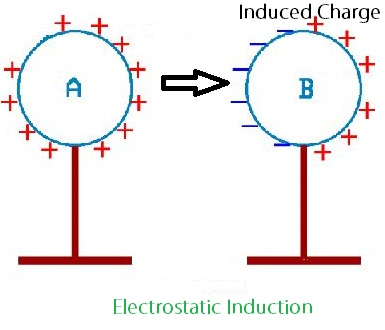
Have you ever experienced the crackling sound of static electricity, especially during the fall and winter seasons? The common phenomenon of electrostatic discharge (ESD) is not as unfamiliar as it may seem. Picture this scenario: as you take off a sweater, you often hear the crackling sound and witness visible discharges. This occurrence is a result of objects with different electrostatic potentials coming into close proximity or direct contact, leading to the transfer of electric charges.
Academic Argumentation:
1.Causes of Electrostatic Discharge
In low humidity, the human body accumulates an electric charge through friction and other factors. This charge can lead to electrostatic discharge when a person with an electric charge comes into contact with equipment. The drier fall and winter seasons exacerbate the prevalence of static electricity during this time.
2.The Purpose of Electrostatic Discharge Test
The electrostatic discharge test serves as a crucial reliability test for electronic products, measuring their ability to resist interference from electrostatic discharge. It simulates scenarios such as the discharge of an operator or object when in contact with equipment and discharge between people or objects.
3. Possible Consequences of Electrostatic Discharges
The repercussions of electrostatic discharges range from direct damage to semiconductor devices caused by energy exchange to changes in electric and magnetic fields, leading to equipment malfunction.
4. Classification of Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic discharge methods are categorized into air discharge and contact discharge. Air discharge involves bringing the charging electrode close to the test equipment, while contact discharge keeps the electrodes in contact with the test equipment during discharge. Contact discharge further divides into direct and indirect methods, simulating personnel near the object of discharge.
5. Electrostatic Discharge Generator Sketch
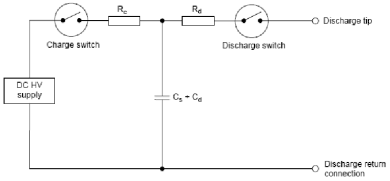
6.Electrostatic Discharge Test Method
During the test, the electrode head of the electrostatic discharge generator must be perpendicular to the equipment's surface. The test is categorized into positive and negative polarity, with the IEC61000-4-2 standard stipulating a minimum of 10 discharges per test point at a 1-second interval. Monitoring the equipment's function before and after the test determines its qualification.
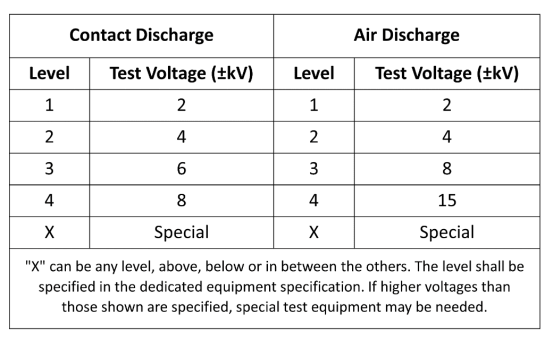
7.Test Severity Level
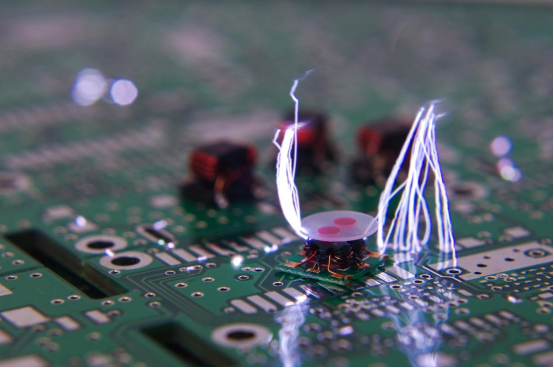
Conclusion:
Understanding and effectively testing for electromagnetic compatibility, particularly in the realm of electrostatic immunity, are paramount in ensuring the reliability of electronic products. By comprehending the causes, purposes, and potential consequences of electrostatic discharges, we pave the way for a safer and more efficient technological landscape. Embracing these insights allows us to develop products that stand resilient against the challenges posed by electrostatic interference, ultimately contributing to the advancement of science and technology.