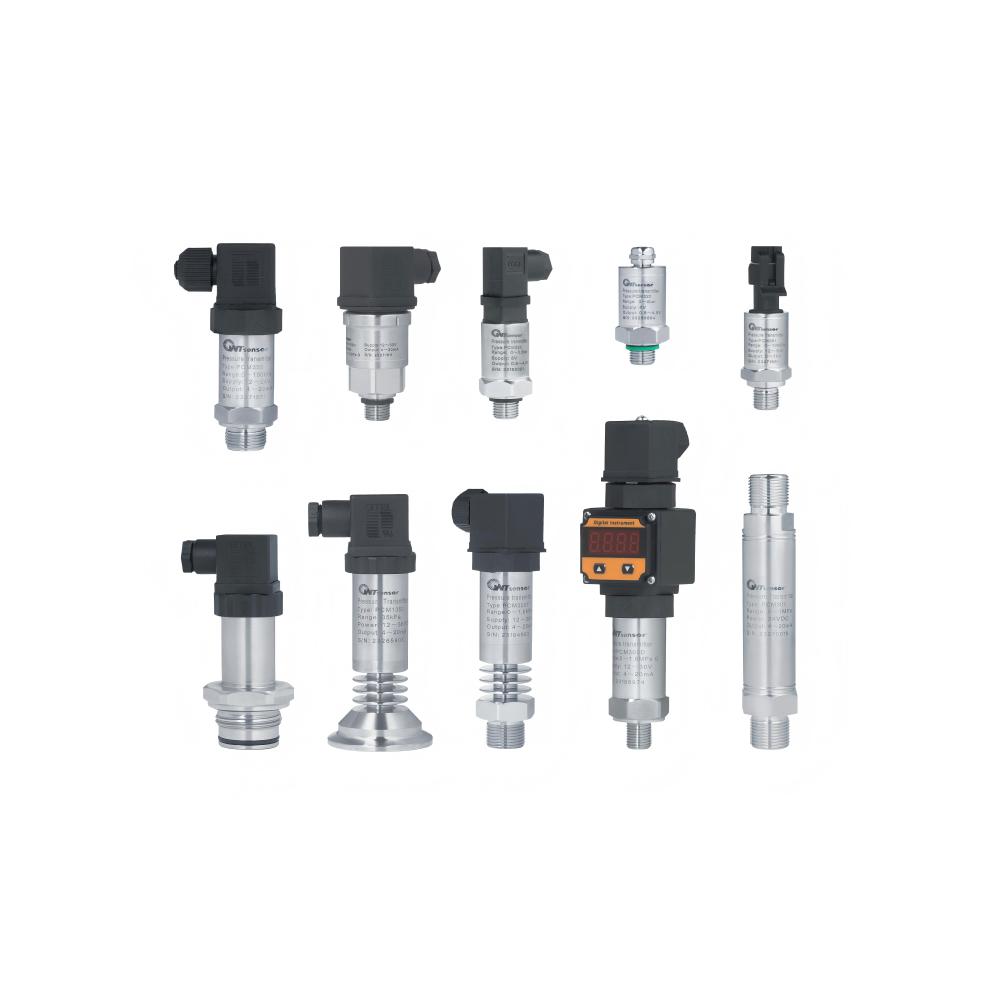
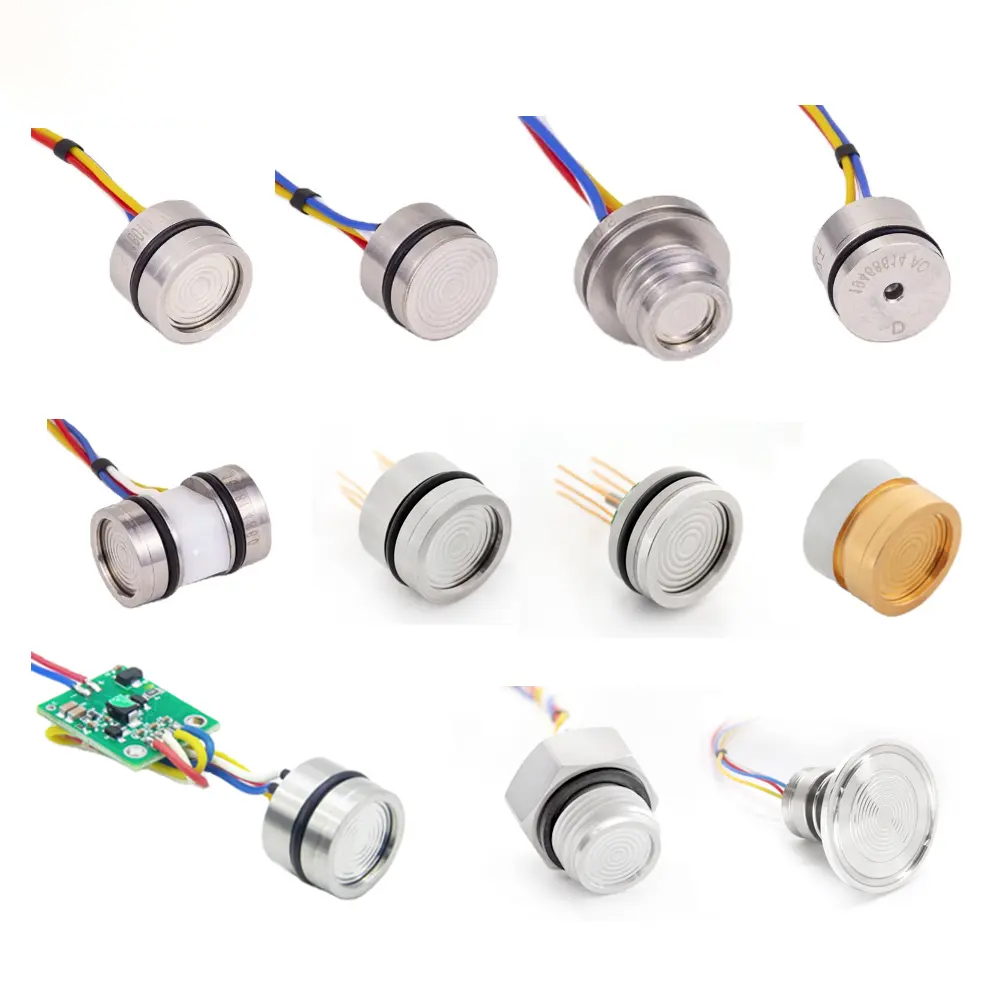
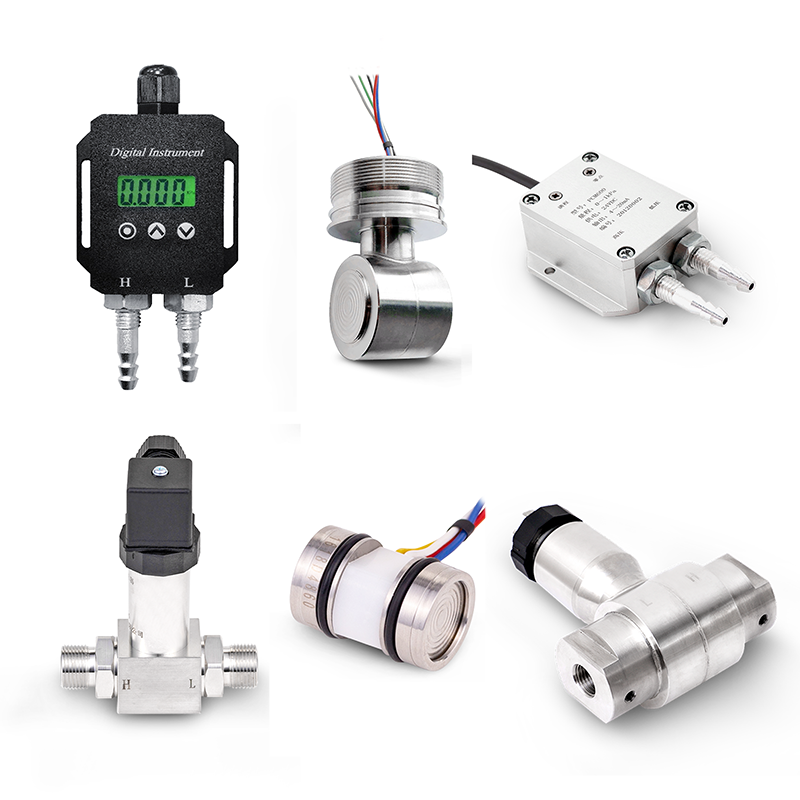
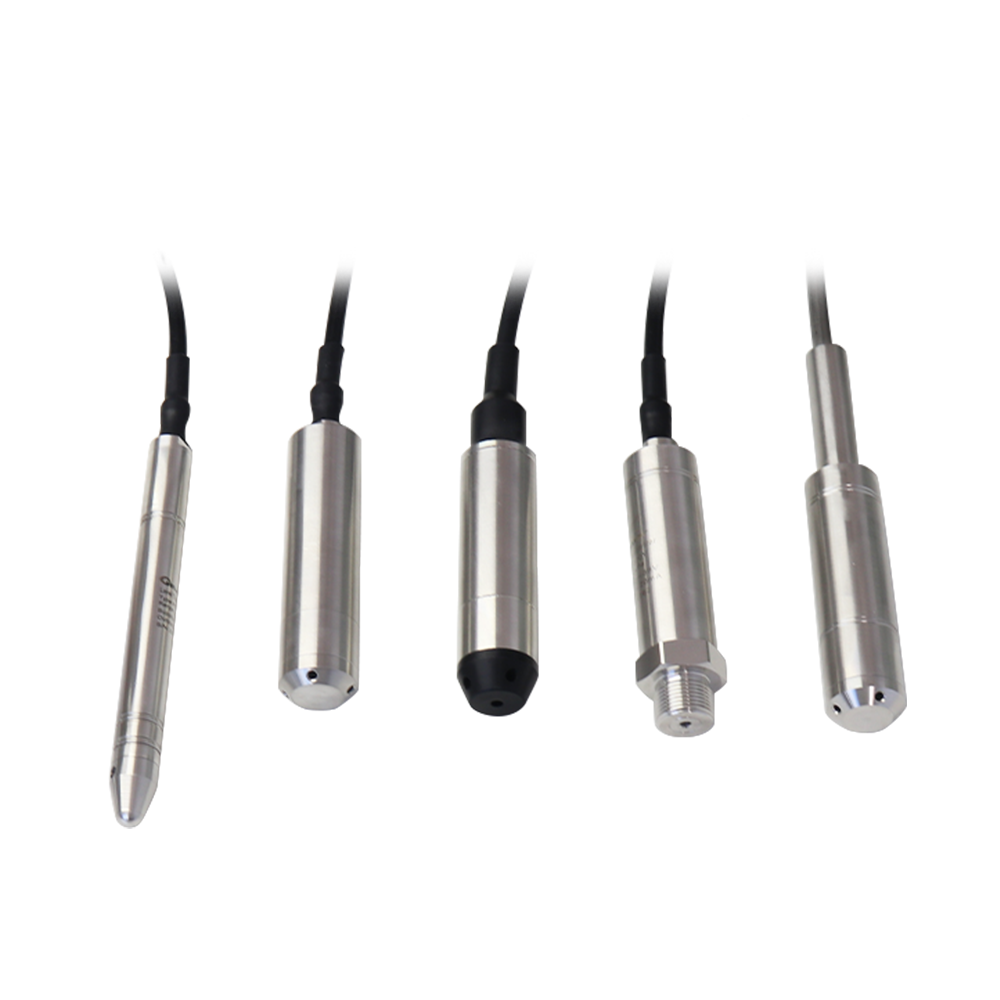
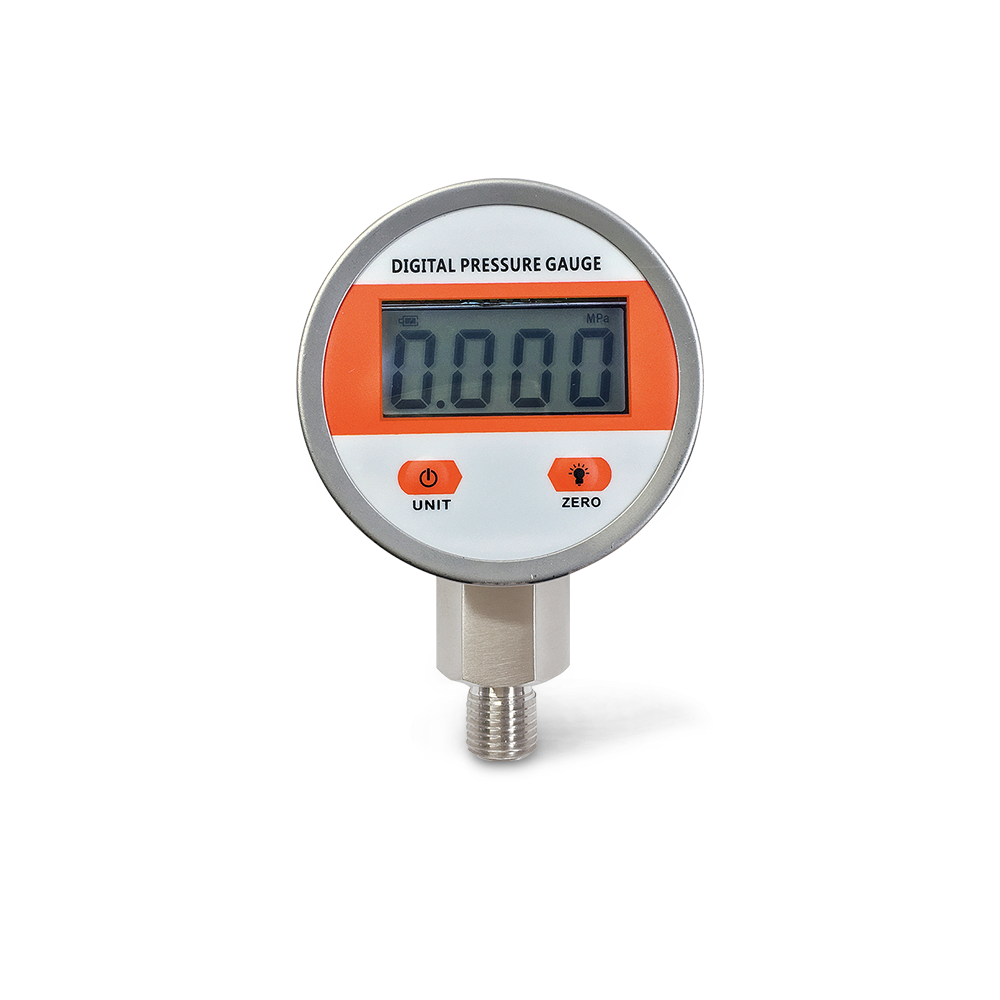
China pressure transmitter, WTsensor pressure sensor
From: Issued date 2023.02.08 Back
We know that there are many types of sensors such as pressure sensors, piezoelectric sensors, ultrasonic sensors, temperature sensors, etc. Let's take a look at the important components of the sensors. What are the pressure types of the sensor (also called pressure sensors)?
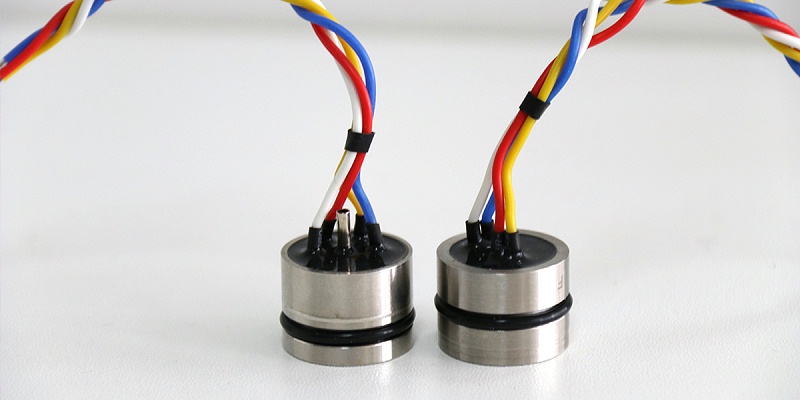
The pressure of the pressure sensor includes: Gauge pressure, Absolute pressure, sealed gauge pressure
Absolute pressure core (A)
Refers to the total pressure acting on the surface area of an object. Its zero point is based on absolute vacuum, also known as total pressure or full pressure.
(1) absolute pressure sensor is used
(2) Reference pressure is vacuum
(3) Whether the physical zero coincides with the electrical zero, which can be customized according to requirements
⑴ 0 ~ 1bar A; 1bar A
When null is zero (± 2mV), the physical zero and electrical zero coincide, and the standard atmospheric pressure is full range.
⑵ 1bar ~ 0bar A
When the standard atmospheric pressure output is zero (± 2mV), the physical zero and electrical zero do not coincide, and the vacuum is full range.
Gauge core (G)
Refers to the total pressure acting on the surface area of an object, and its zero point is based on the local atmospheric pressure as the reference point.
Gauge pressure sensor is used
Reference pressure is the current atmospheric pressure
The physical zero and electrical zero coincide
E. g ⑴ 0 ~ 2.5MPa G, 2.5MPa G
Under the atmospheric pressure, the output is zero (± 2mV), and the pressure is 2.5MPa at atmospheric pressure for full range.
Sealed gauge pressure (S)
Refers to the medium in the sealing device, which is at the actual pressure of the medium when it will leak.
(1) absolute pressure sensor is used
⑵ Reference pressure is standard atmospheric pressure
(3) The physical zero point and the electrical zero point do not coincide. By changing the resistance value of the zeroing resistance of the compensation circuit, the core body output is ± 2mV under standard atmospheric pressure.
E.g
⑴ 0MPa ~ 10MPa S; 10MPa S
When the atmospheric pressure output is zero (± 2mV), the full range is added when 10MPa is added.
⑵ -0.1bar ~ 0.3bar S
When the output is -0.1bar (vacuum) at zero (± 2mV), add 0.3bar at atmospheric pressure for full range.